AWS Security Hub scanner reference for STO
You can scan your configurations using AWS Security Hub, which provides a comprehensive view of your security state in AWS and helps you check your environment against security industry standards and best practices.
Important notes for running AWS Security Hub scans in STO
Docker-in-Docker requirements
The following use cases require a Docker-in-Docker background step in your pipeline:
- Container image scans on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for Orchestration and Dataload scan modes
- Security steps (not step palettes) on Kubernetes and Docker build infrastructures
- Required for all target types and Orchestration/DataLoad modes
The following use cases do not require Docker-in-Docker:
- Harness Cloud AMD64 build infrastructures
- SAST/DAST/configuration scans that use scanner templates (not Security steps)
- Ingestion scans where the data file has already been generated
Set up a Docker-in-Docker background step
-
Go to the stage where you want to run the scan.
-
In Overview, add the shared path
/var/run. -
In Execution, do the following:
-
Click Add Step and then choose Background.
-
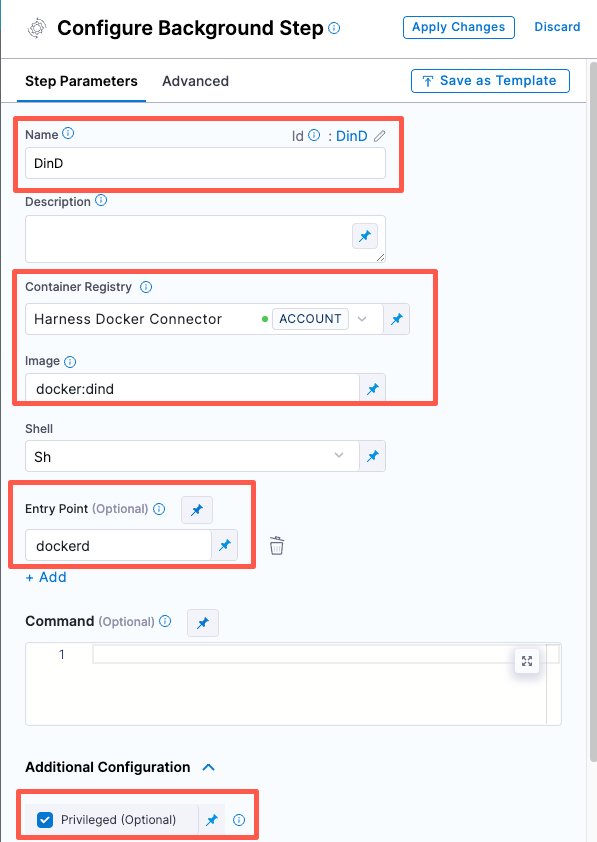
Configure the Background step as follows:
-
Dependency Name =
dind -
Container Registry = The Docker connector to download the DinD image. If you don't have one defined, go to Docker connector settings reference.
-
Image =
docker:dind -
Under Entry Point, add the following:
dockerdIn most cases, using
dockerdis a faster and more secure way to set up the background step. For more information, go to the TLS section in the Docker quick reference.
If the DinD service doesn't start with
dockerd, clear the Entry Point field and then run the pipeline again. This starts the service with the default entry point.- Under Optional Configuration, select the Privileged checkbox.
-
-
- Visual setup
- YAML setup
Add a Background step to your pipeline and set it up as follows:
- step:
type: Background
name: background-dind-service
identifier: Background_1
spec:
connectorRef: CONTAINER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: docker:dind
shell: Sh
entrypoint:
- dockerd
privileged: true
Root access requirements
You need to run the scan step with root access if either of the following apply:
-
You need to run a Docker-in-Docker background service.
-
You need to add trusted certificates to your scan images at runtime.
You can set up your STO scan images and pipelines to run scans as non-root and establish trust for your own proxies using self-signed certificates. For more information, go to Configure STO to Download Images from a Private Registry.
For more information
The following topics contain useful information for setting up scanner integrations in STO:
AWS Security Hub step configuration
Scan
Scan Mode
- Extraction Configure the step to extract scan results from an external SaaS service and then ingest, normalize, and deduplicate the data.
- Ingestion Configure the step to read scan results from a data file and then ingest, normalize, and deduplicate the data.
Scan Configuration
The predefined configuration to use for the scan. All scan steps have at least one configuration.
Target
Type
- Configuration Scan your cloud environment by gathering configuration data via the cloud provider’s APIs.
Name
The identifier for the target, such as codebaseAlpha or jsmith/myalphaservice. Descriptive target names make it much easier to navigate your scan data in the STO UI.
It is good practice to specify a baseline for every target.
Variant
The identifier for the specific variant to scan. This is usually the branch name, image tag, or product version. Harness maintains a historical trend for each variant.
Ingestion File��
The path to your scan results when running an Ingestion scan, for example /shared/scan_results/myscan.latest.sarif.
-
The data file must be in a supported format for the scanner.
-
The data file must be accessible to the scan step. It's good practice to save your results files to a shared path in your stage. In the visual editor, go to the stage where you're running the scan. Then go to Overview > Shared Paths. You can also add the path to the YAML stage definition like this:
- stage:
spec:
sharedPaths:
- /shared/scan_results
Authentication
You should create Harness text secrets with your encrypted access ID and token and access them using the format <+secrets.getValue("project.my-secret")>.
Access ID
The access ID for your AWS account.
Access Token
The access token for your AWS account.
Log Level, CLI flags, and Fail on Severity
Log Level
The minimum severity of the messages you want to include in your scan logs. You can specify one of the following:
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARNING
- ERROR
Additional CLI flags
You can use this field to customize the scan with specific command-line arguments supported by that scanner.
Fail on Severity
Every Security step has a Fail on Severity setting. If the scan finds any vulnerability with the specified severity level or higher, the pipeline fails automatically. You can specify one of the following:
CRITICALHIGHMEDIUMLOWINFONONE— Do not fail on severity
The YAML definition looks like this: fail_on_severity : critical # | high | medium | low | info | none