Input sets and overlays
With input sets and overlays, you can reuse a single pipeline for multiple scenarios. You can define each scenario in an input set or overlay, and then select the relevant input set or overlay at runtime.
Input sets are collections of runtime input values for a pipeline. Runtime inputs provide placeholders with the expectation that you'll define those values at runtime.
Runtime inputs are useful for templatizing your pipelines, because runtime inputs can have different values each time the pipeline runs. For example, you can set all infrastructure settings to runtime input so that users provide relevant dev, QA, or prod values with each run. This way, users don't need to edit the actual pipeline, they just supply the necessary values for that run.
Input sets make it even easier to templatize with runtime inputs. Input sets contain preconfigured values for any settings in the pipeline that use runtime input. Instead of manually entering a value for each runtime input, you select the input set that contains the relevant values. You can create input sets for different pipeline use cases, and then select the relevant input set at runtime. When other users run the same pipeline, they can select the input set that corresponds with their use case.
Input sets reduce the chance of errors in runtime input by eliminating the need to manually populate each runtime input value.
Overlays are groups of input sets, which enable you to pull runtime inputs from multiple input sets.
Specify settings that use runtime input
To be included in an input set, settings must be configured to use runtime input. Settings that don't use runtime input can't be included in input sets. You can configure runtime input in either the Visual or YAML editors in the Pipeline Studio.
- Visual editor
- YAML editor
In the Pipeline Studio's Visual Editor, you can use the Value type selector to select Runtime Input.
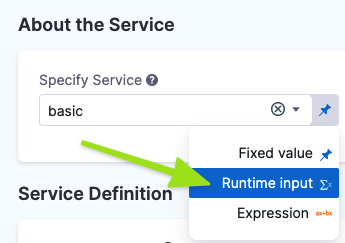
In free-text fields, you can directly enter <+input> to specify runtime input without changing the value type.
When writing pipelines in YAML, enter <+input> for a setting's value to indicate runtime input.
- step:
identifier: Run_1
type: Run
name: Run_1
spec:
shell: <+input>
command: <+input>
Almost any setting in a pipeline can use runtime input, including variables, artifacts, connectors, environments, infrastructures, services, secrets, step settings, looping strategies, and more.
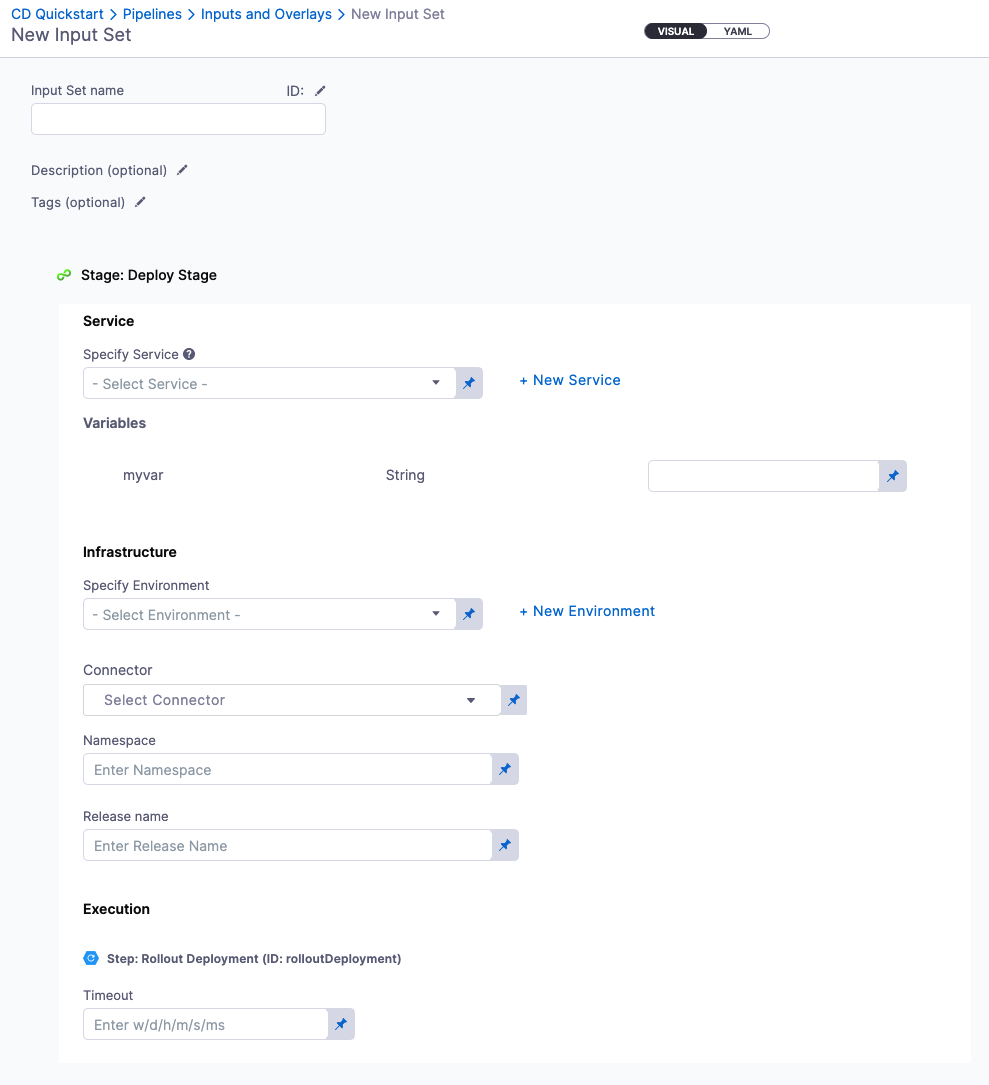
Create input sets
-
In the Pipeline Studio header, select Input Sets.
-
Select New Input Set.
-
Enter a Name for the input set. Description and Tags are optional.
-
Enter values for the settings that use runtime input, and then select Save.
If a setting doesn't use runtime input (
<+input>), you can't define a value for it in an input set.You don't have to provide a value for every setting. For example, you can leave some settings as manul runtime input. Or you can create multiple input sets that populate different values, which you can then combine into overlays.
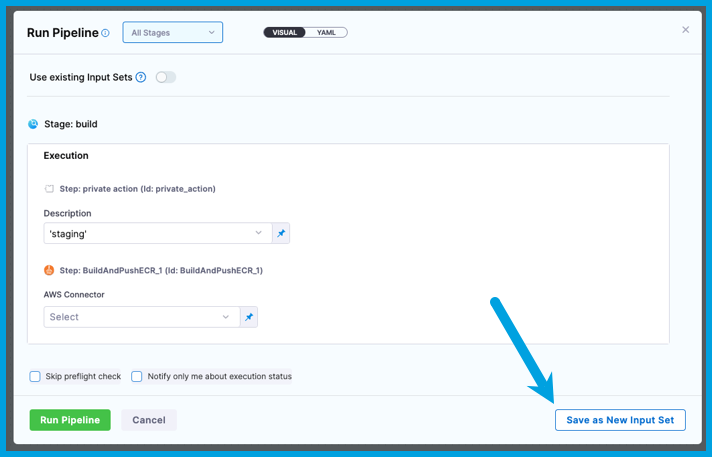
Create input sets at runtime
When you run a pipeline that requires runtime input, you can select Save as New Input Set to quickly create an input set from your provided values.
Create input sets in YAML
You can use the YAML editor to write input sets. When creating an input set, select YAML to switch to the YAML editor.
Here is an example of a YAML definition for an input set for a Deploy stage. This input set specifies the service to deploy, as well as the primary artifact reference, and the value of the replicas variable.
inputSet:
name: Artifact Input Set
tags: {}
identifier: Artifact_Input_Set
orgIdentifier: default
projectIdentifier: CD_Docs
pipeline:
identifier: kubernetes_demo
stages:
- stage:
identifier: k8s_deployment
type: Deployment
spec:
service:
serviceRef: Kubernetes
serviceInputs:
serviceDefinition:
type: Kubernetes
spec:
artifacts:
primary:
primaryArtifactRef: nginx
sources: ""
variables:
- name: replicas
type: String
value: "3"
Import input sets
With the Harness Git Experience, you can also import input sets from a Git repo.
Create overlays
You can combine multiple input sets into overlays, and then, when you run the pipeline, you choose which input sets to use for that run. With overlays, you don't have to define every runtime input value in every input set, providing a flexible, "build-your-own" input set experience.
For example, assume you have a CD pipeline that is used for multiple services. The services have some common configurations, but there are some differences. You can create an overlay consisting of multiple input sets so that users can pick and choose the input sets that correspond with their deployment scenario:
- One input set for the common or default configurations. This set should be used for every run, regardless of the selected service.
- Input sets for each service. Each of these input sets contains the configurations for that service. These input sets can modify values defined in the default input set, and they can provide values for empty fields that weren't specified in the default input set.
- Input sets for edge cases, such as an input set that contains a specific build number.
Configure overlays��
To configure overlays:
- Create input sets.
- On the Input Sets page, select New Input Set, and then select Overlay Input Set.
- Enter a Name for the overlay. Description and Tags are optional.
- In Use existing Input Sets, select the input sets to include in this overlay, and select Apply Input Sets
- Drag and drop the input sets to define their priority in the overlay.
- Select Save.
Priority in overlays
In an overlay, you specify the order in which to resolve the input sets. The first input set in the sequence is resolved first. Then, input sets resolved after the first either replace values specified in prior input sets or populate values not specified in prior input sets.
If a setting is specified in multiple input sets, the value is replaced as each input set is resolved, and the setting's final value is the value assigned in the last input set to be resolved.
Manage access to input sets
Currently, input set access control is behind the feature flag PIE_INPUTSET_RBAC_PERMISSIONS. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature. We will also run a migration for you so that existing input sets remain accessible to users.
Input sets can be access-controlled, similar to pipelines and other entities. This allows you to make some input sets invisible to certain users, or not let them edit the values in the input sets. The permissions for input sets are View, Create/Edit, and Delete. You can view and manage these permissions on the Roles page under Access Control.
Input sets are listed along with other resources in the Resource Group section of the Access Control screens. For more information on setting up and managing permissions using Resource Groups and Roles, go to Manage resource groups.
To use an input set for a pipeline execution, the user must have View permissions on the input set, along with Execute permissions for the pipeline. To edit the input set, the user must have Edit permissions for the input set.
When a user creates a new input set, Create/Edit and View permissions are added by default for the user.
Run pipelines with input sets or overlays
To run a pipeline with an input set or overlay:
-
In the Pipeline Studio, select Run.
-
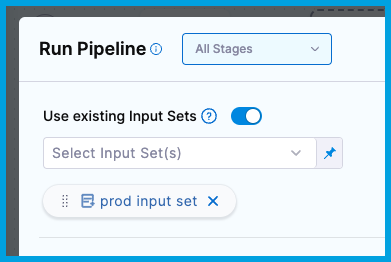
On the Run Pipeline window, select Use existing Input Sets.
-
Select input sets or overlays to use for the run.
-
On the Run Pipeline window, the settings that require runtime input are populated with the values from the selected input sets. If necessary, you can manually change any of the values before running the pipeline.
-
Select Run Pipeline.
You can also run a pipeline with an input set or overlay from the Input Sets page.
Value resolution
When you select input sets or overlays to use for a pipeline run, Harness applies the values from the input sets to their corresponding pipeline settings. With an overlay, the values are resolved according to the specified priority in the overlay.
For each setting that requires runtime input, Harness either:
- Displays the value assigned to the setting, as resolved from the input sets.
- Displays an error for any required settings that don't have a value assigned.
If any required settings don't have a value, you must manually input a value before you can run the pipeline.